インターネットを使ったWebアプリケーションでは、相手(サーバとクライアント)の認証と、通信データの暗号化のため、プロコトルにTLS(Transport Layer Security)/SSL(Secure Socket Layer)が使われます。
認証には、サーバの正当性を確認するためのサーバ認証と、クライアントの正当性を確認するための2つの方法があります。
一般的には、インターネット上のサーバにアクセスする場合には、接続する先のサーバの正当性を確認するために、サーバ認証が行われます。
ただし、接続されるサーバにおいても、クライアントの正当性を確認したい場合、サーバ認証に加えてクライアント認証も行われます。
例えば、サーバに接続できる端末やアプリケーションを限定する必要がある場合、あらかじめ鍵ペアとクライアント証明書を端末やアプリケーションに登しておき、クライアント認証を実施します。
認証が正常に行われ、TLS/SSLのセッションが確立された後、送受信されるすべてのデータが暗号化されます。
■ 主なバージョン
TLSとSSLは、同じものですが、TLSはSSLより後発で、暗号アルゴリズムの強度が上がっています。
これまで使われてきた主なバージョンは、古い順に並べると以下となります。
SSL3.0
TLS1.0
TLS1.2
TLS1.3
現時点では、TLS1.2以上が主流となりつつ時期ですが、いまだTLS1.0も使われています。
これらのバージョンは、社会で発生するリスクに応じて、推奨されるバージョンが上がっていきます。
■ クライアント認証とサーバ認証のシーケンス
TLS/SSLのシーケンス(シェークハンドと呼ばれます)は、TCPでコネクションを確立した後、以下の手順で実施されます。
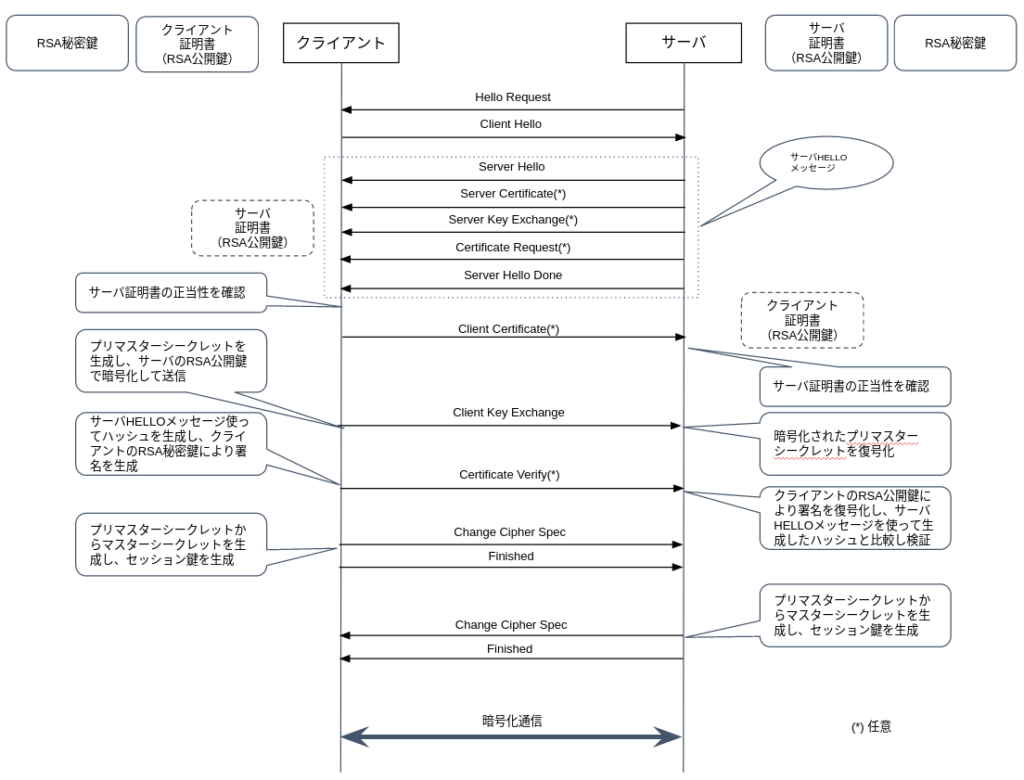
認証は、公開鍵暗号化方式(RSA)を使って行われ、データの暗号化はセッション鍵により処理速度の早いAESなどの共通鍵暗号化方式を使って行われます。
クライアントには、クライアント証明書とRSA秘密鍵、サーバには、サーバ証明書とRSA秘密鍵を保持します。
クライアントはサーバ証明書を取得し署名を検証します。サーバはクライアント証明書を取得し、署名を検証します。
さらに、クライアントは、サーバへサーバHELLOメッセージの署名を送信し、サーバでは、その署名を検証することで、クライアントを認証します。
クライアントとサーバでプリマスターシークレットを共有し、マスターシークレットを生成後、お互いに同じセッション鍵を生成し、暗号化通信を開始します。
■ 実践
サーバにApache、クライアントにPythonプログラムと使ったサーバ認証とクライアント認証の両方を実施します。
1)仮のCA局を生成し、CA局の鍵ペアと証明書を作成する
testcaディレクトリを作成し、その配下に、newcerts、privateディレクトリを作成します。
さらに、index.txt、index.txt.attrの空ファイルを作成し、
00を初期値とするserialファイルを作成します。
$ mkdir testca
$ cd testca
S cd testca
testca$ touch index.txt
testca$ touch index.txt.attr
testca$ echo 00 > serial
testca$ tree
.
├── index.txt
├── index.txt.attr
├── serial
├── newcerts
└── private
testca/private配下に、CA局の鍵ペアを生成します。
testca/private$ openssl genrsa 2048 > cakey.key
Generating RSA private key, 2048 bit long modulus (2 primes)
…………………………………………………………..+++++
………………………………………………………………………………………………….+++++
e is 65537 (0x010001)
testca配下に、CA局の証明書発行のためのCSRを生成します。
testca$ openssl req -new -key private/cakey.key -out cakey.csr
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]:JP
State or Province Name (full name) [Some-State]:tokyo
Locality Name (eg, city) []:minato
Organization Name (eg, company) [Internet Widgits Pty Ltd]:test
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:test
Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []:test.com
Email Address []:test@test.com
Please enter the following 'extra' attributes
to be sent with your certificate request
A challenge password []:
An optional company name []:testca配下にCA局の証明書を生成します。
testca$ openssl x509 -days 365 -req -signkey private/cakey.key -in cakey.csr -out cacert.crt
Signature ok
subject=C = JP, ST = tokyo, L = minato, O = test, OU = test, CN = test.com, emailAddress = test@test.com
Getting Private key2)サーバの鍵ペアと証明書を作成する
次に、testca配下にサーバのドメイン(test.jp)のフォルダを作成します。certs、privateディレクトリを作成します。
また、testca配下に以下のサーバ用のドメイン情報を記載したsan.txtファイルを作成します。
subjectAltName=DNS:*.test.jp, DNS:test.jptestca配下は以下のようなディレクトリ・ファイル構成となります。
testca$ tree
.
├── index.txt
├── index.txt.attr
├── newcerts
├── private
├── san.ext
├── serial
└── test.jp
├── certs
└── private
testca/test.jp/private配下に、サーバの鍵ペアを生成します。
testca$ openssl genrsa 2048 > ./test.jp/private/server.keytestca/test.jp/certs配下に、サーバの証明書発行のためのCSRを生成します。
testca$ openssl req -new -key ./test.jp/private/server.key -out ./test.jp/certs/server.csr
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]:JP
State or Province Name (full name) [Some-State]:tokyo
Locality Name (eg, city) []:minato
Organization Name (eg, company) [Internet Widgits Pty Ltd]:test
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:test
Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []:test.jp
Email Address []:
Please enter the following 'extra' attributes
to be sent with your certificate request
A challenge password []:
An optional company name []:testca/test.jp/certs配下にサーバ証明書を生成します。(CA局の署名つき)
※)openssl.cnfの以下のデフォルトCAのパスを設定しておくこと
[ CA_default ]
dir = <testcaのパス>
testca$ openssl ca -keyfile ./private/cakey.key -cert ./cacert.crt -in ./test.jp/certs/server.csr -out ./test.jp/certs/server.crt -days 825 -outdir ./newcerts -extfile ./san.ext
Using configuration from /home/swata/anaconda3/ssl/openssl.cnf
Check that the request matches the signature
Signature ok
Certificate Details:
Serial Number: 0 (0x0)
Validity
Not Before: Mar 11 11:23:04 2023 GMT
Not After : Jun 13 11:23:04 2025 GMT
Subject:
countryName = JP
stateOrProvinceName = tokyo
organizationName = test
organizationalUnitName = test
commonName = test.jp
emailAddress = test@test.jp
X509v3 extensions:
X509v3 Subject Alternative Name:
DNS:*.test.jp, DNS:test.jp
Certificate is to be certified until Jun 13 11:23:04 2025 GMT (825 days)
Sign the certificate? [y/n]:y
1 out of 1 certificate requests certified, commit? [y/n]y
Write out database with 1 new entries
Data Base Updated3)クライアントの鍵ペアと証明書を作成する
次に、testca配下にクライアントのドメイン(test_cl.jp)のフォルダを作成します。certs、privateディレクトリを作成します。
また、testca配下に以下のサーバ用のドメイン情報を記載したsan.txtファイルを作成します。
subjectAltName=DNS:*.test_cl.jp, DNS:test_cl.jp
testca配下は以下のようなディレクトリ・ファイル構成となります。
S:~/testca$ tree
.
├── cacert.crt
├── cakey.csr
├── index.txt
├── index.txt.attr
├── index.txt.attr.old
├── index.txt.old
├── newcerts
│ ├── 00.pem
│ └── 01.pem
├── private
│ ├── cakey.key
│ └── server.key
├── san.ext
├── serial
├── serial.old
├── test.jp
│ ├── certs
│ │ ├── server.crt
│ │ └── server.csr
│ └── private
│ └── server.key
└── test_cl.jp
├── certs
└── private
testca/test_cl.jp/private配下に、クライアントの鍵ペアを生成します。
testca$ openssl genrsa 2048 > ./test_cl.jp/private/client.key
Generating RSA private key, 2048 bit long modulus (2 primes)
.....+++++
....+++++
e is 65537 (0x010001)testca/test_cl.jp/certs配下に、クライアントの証明書発行のためのCSRを生成します。
testca$ openssl req -new -key ./test_cl.jp/private/client.key -out ./test_cl.jp/certs/client.csr
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]:JP
State or Province Name (full name) [Some-State]:tokyo
Locality Name (eg, city) []:minato
Organization Name (eg, company) [Internet Widgits Pty Ltd]:test
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:test_cl
Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []:test_cl.jp
Email Address []:test_cl@test_cl.jp
Please enter the following 'extra' attributes
to be sent with your certificate request
A challenge password []:
An optional company name []:testca/test_cl.jp/certs配下にクライアント証明書を生成します。(CA局の署名つき)
※)openssl.cnfの以下のデフォルトCAのパスを設定しておくこと
[ CA_default ]
dir = <testcaのパス>
testca$ openssl ca -keyfile ./private/cakey.key -cert ./cacert.crt -in ./test_cl.jp/certs/client.csr -out ./test_cl.jp/certs/client.crt -days 825 -outdir ./newcerts -extfile ./san.ext
Using configuration from /home/swata/anaconda3/ssl/openssl.cnf
Check that the request matches the signature
Signature ok
Certificate Details:
Serial Number: 1 (0x1)
Validity
Not Before: Mar 11 11:38:41 2023 GMT
Not After : Jun 13 11:38:41 2025 GMT
Subject:
countryName = JP
stateOrProvinceName = tokyo
organizationName = test
organizationalUnitName = test_cl
commonName = test_cl.jp
emailAddress = test_cl@test_cl.jp
X509v3 extensions:
X509v3 Subject Alternative Name:
DNS:*.test.jp, DNS:test.jp
Certificate is to be certified until Jun 13 11:38:41 2025 GMT (825 days)
Sign the certificate? [y/n]:y
1 out of 1 certificate requests certified, commit? [y/n]y
Write out database with 1 new entries
Data Base Updatedtestca配下は以下のようなディレクトリ・ファイル構成となります。
testca$ tree
.
├── cacert.crt
├── cakey.csr
├── index.txt
├── index.txt.attr
├── index.txt.attr.old
├── index.txt.old
├── newcerts
│ ├── 00.pem
│ └── 01.pem
├── private
│ ├── cakey.key
│ └── server.key
├── san.ext
├── serial
├── serial.old
├── test.jp
│ ├── certs
│ │ ├── server.crt
│ │ └── server.csr
│ └── private
│ └── server.key
└── test_cl.jp
├── certs
│ ├── client.crt
│ └── client.csr
└── private
└── client.key4)UbuntuでのApacheの設定(サーバ認証とクライアント認証)
/etc/apache2/sites-available/default-ssl.confのSSLCertificateFileとSSLCertificateKeyFileにサーバ証明書ファイルとサーバ鍵ペアファイルのパスを記載します。
また、SSLVerifyClientを"require"とすることでクライアント認証を有効にし、
CA局の証明書にてチェックできるように、SSLVerifyDepthに"1"、SSLCACertificateFileにCA局の証明書ファイルのパスを設定します。
<IfModule mod_ssl.c>
<VirtualHost _default_:443>
ServerAdmin webmaster@localhost
DocumentRoot /var/www/html
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined
SSLEngine on
SSLCertificateFile /home/swata/testca/test.jp/certs/server.crt
SSLCertificateKeyFile /home/swata/testca/test.jp/private/server.key
SSLCACertificateFile /home/swata/testca/cacert.crt
SSLVerifyClient require
SSLVerifyDepth 1
<FilesMatch "\.(cgi|shtml|phtml|php)$">
SSLOptions +StdEnvVars
</FilesMatch>
<Directory /usr/lib/cgi-bin>
SSLOptions +StdEnvVars
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
</IfModule>
ApacheのSSL機能を有効にし、再起動します。
$ sudo a2enmod ssl
Considering dependency setenvif for ssl:
Module setenvif already enabled
Considering dependency mime for ssl:
Module mime already enabled
Considering dependency socache_shmcb for ssl:
Enabling module socache_shmcb.
Enabling module ssl.
See /usr/share/doc/apache2/README.Debian.gz on how to configure SSL and create self-signed certificates.
To activate the new configuration, you need to run:
systemctl restart apache2
$ sudo systemctl restart apache25)クライアントからのサーバ認証とクライアント認証によるHTTPS接続
サーバのドメイン名:test.jpで接続するため、/etc/hostsに以下を追記しておきます。
[/etc/hosts]
# test local server
127.0.0.1 test.jp
以下にサーバ認証とクライアント認証によるHTTPS接続のコードを示します。
クライアントの証明書と鍵ペア、そして、CA局の証明書を指定し、サーバのドメイン名で接続します。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import requests
# path of key and cert files.
path = 'testca/'
# client cert file
crt = path+"test_cl.jp/certs/client.crt"
# client key file
key = path+"test_cl.jp/private/client.key"
# ca cert file
crt_ca = path+"cacert.crt"
# server url
endpoint = "https://test.jp/"
# connect to server.
response=requests.get(endpoint, cert=(crt,key),verify=crt_ca)
print(response.text)■ まとめ
クライアントをサーバで特定するには、サーバ認証に加えクライアント認証が必要になります。
HTTPのBASIC認証(ユーザIDとパスワード)を使ってクライアントを認証する方法もありますが、クライアント証明書を使う方法のほうが、操作不要であり、PKIの仕組みを使うという点でセキュリティ面で優れています。
ただし、別途、クライアント証明書と鍵ペアを発行し、クライアントにダウンロードさせる仕組みが必要になり、期限の管理も含め、運用面は負担が大きくなる点がデメリットです。
ソフトウェア開発・システム開発業務/セキュリティ関連業務/ネットワーク関連業務/最新技術に関する業務など、「学習力×発想力×達成力×熱意」で技術開発の実現をサポート。お気軽にお問合せ下さい






